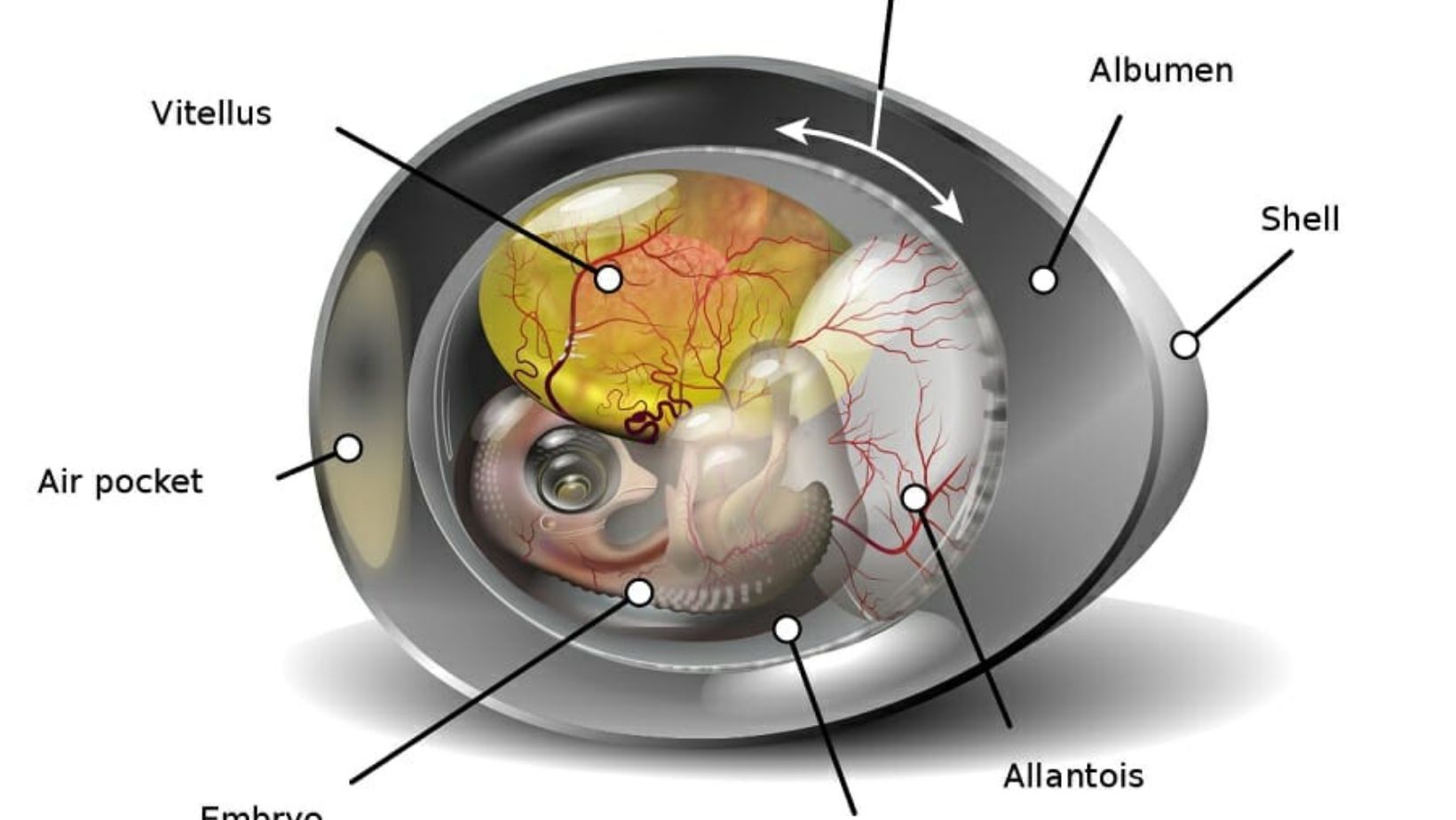
Selaput Pembungkus Embrio Salah Satunya Adalah Amnion Yang Mempunyai Fungsi
As an expert in embryology, I delve into the intricate structures that envelop and protect developing embryos, one of which is the amnion Selaput Pembungkus Embrio Salah Satunya Adalah Amnion Yang Mempunyai Fungsi. The amnion plays a crucial role in supporting and safeguarding the growing embryo during pregnancy. This membranous sac is filled with amniotic fluid, providing a cushion against external forces and maintaining a stable environment for fetal development.
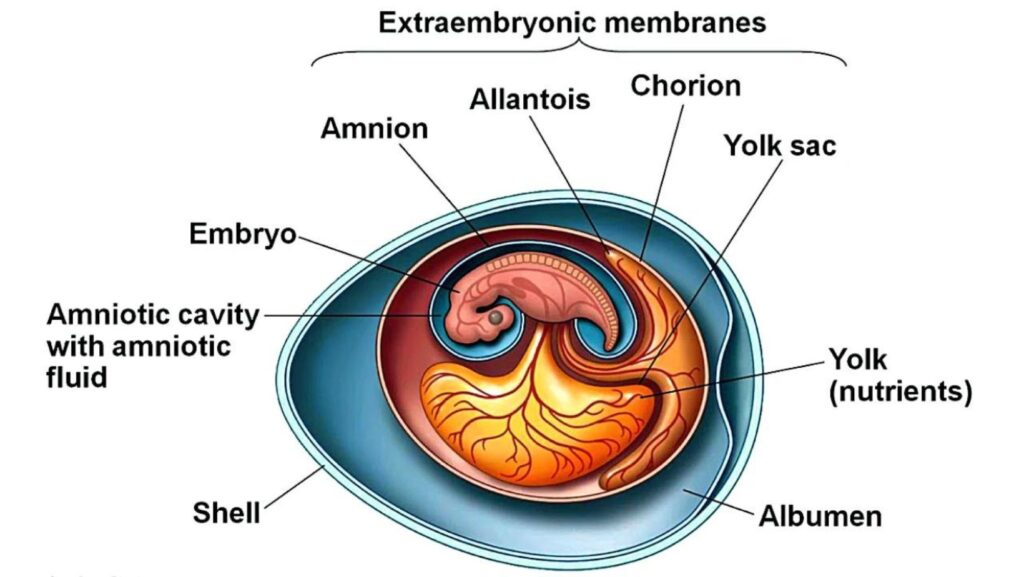
It’s fascinating to explore the functions of the amnion within the realm of embryonic development. Not only does it serve as a protective barrier against mechanical shocks, but it also helps regulate temperature and prevent desiccation. This vital structure contributes significantly to the overall well-being of the developing fetus throughout gestation.
Understanding the significance of the amnion sheds light on its pivotal role in prenatal care and maternal health Selaput Pembungkus Embrio Salah Satunya Adalah Amnion Yang Mempunyai Fungsi. By unraveling the mysteries surrounding this protective membrane, we gain deeper insights into how nature orchestrates the process of human reproduction with remarkable precision and complexity.
Functions of the Amnion as One of the Embryo’s Protective Membranes
The amnion, a crucial protective membrane surrounding the developing embryo, plays several vital roles in ensuring the well-being and development of the growing fetus. Let’s delve into some key functions that highlight the significance of the amnion:
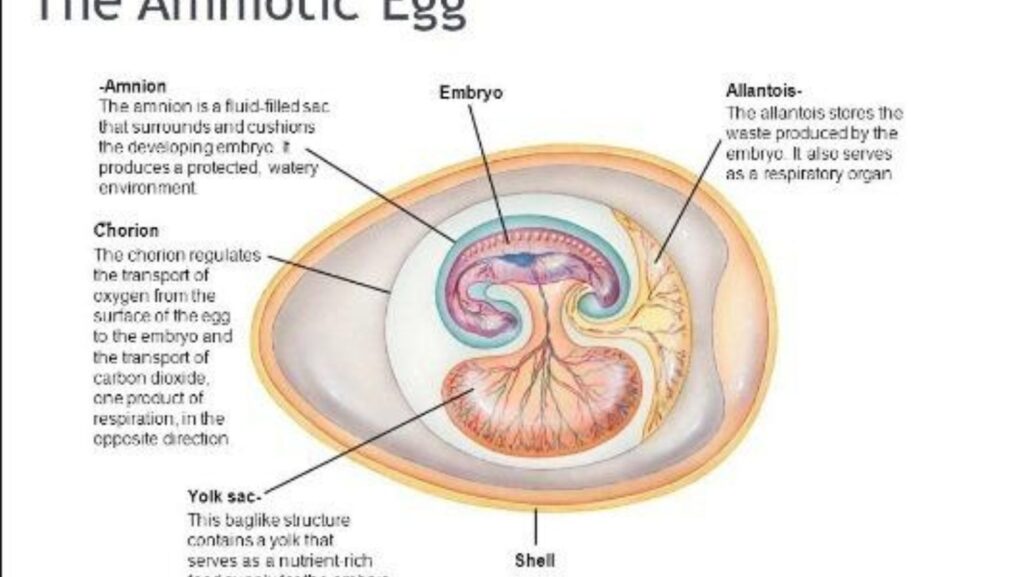
- Protection: One primary function of the amnion is to provide a secure environment for the developing embryo by acting as a physical barrier against external harm. It shields the fetus from mechanical injuries, infections, and temperature fluctuations.
- Fluid Regulation: The amniotic fluid enclosed by the amnion serves multiple purposes such as cushioning against physical shocks, aiding in fetal movement, preventing compression of umbilical cord vessels, and contributing to proper lung development through fetal swallowing.
- Nutrient Transport: Another vital role of the amniotic membrane is facilitating nutrient exchange between mother and fetus. Through this process, essential substances like oxygen and nutrients are transported to the fetus while waste products are carried away.
- Developmental Support: The amnion also supports embryonic growth by allowing sufficient space for movement and preventing adhesions between fetal tissues. This freedom of movement within a protective environment is crucial for normal musculoskeletal development.
- Immunological Protection: Additionally, recent research suggests that apart from physical protection, the amniotic membrane may possess immunological properties that help regulate maternal-fetal immune tolerance and protect against microbial threats during pregnancy.
These functions collectively underscore the critical role played by the amnion in nurturing and safeguarding embryonic development within an intricate biological system designed to support life.
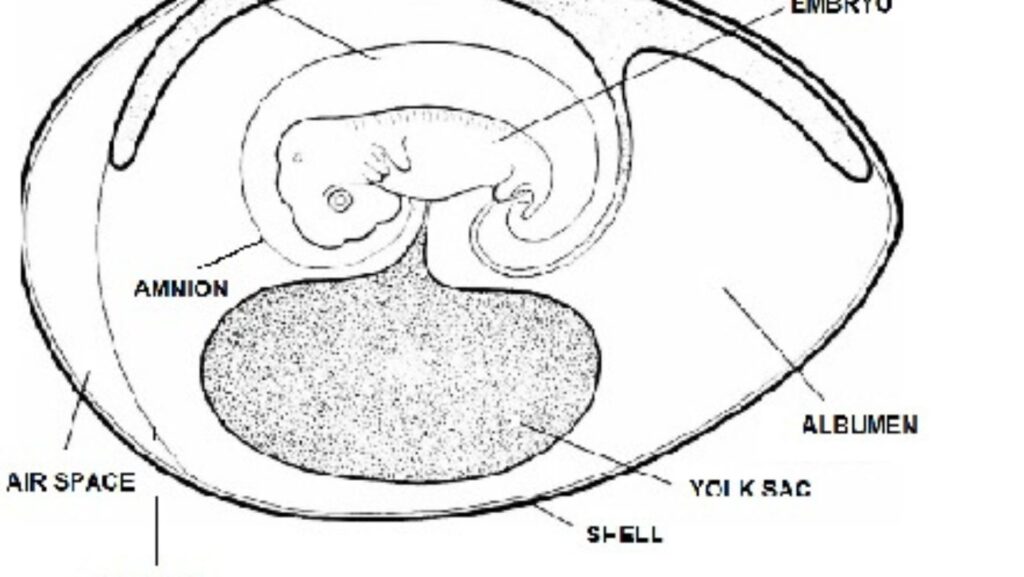
Development and Structure of the Amnion
The amnion, a crucial embryonic membrane Selaput Pembungkus Embrio Salah Satunya Adalah Amnion Yang Mempunyai Fungsi, plays a vital role in protecting and nourishing the developing fetus. Let’s delve into the fascinating world of amnion development and structure.
Formation Process
- The amnion originates from the embryonic ectoderm, specifically from the epiblast layer.
- Around day 8 to 9 post-fertilization, the epiblast cells form a thin, transparent membrane known as the amnion.
- This membrane expands rapidly to envelop the embryo completely within its fluid-filled cavity called the amniotic sac.
- The amniotic fluid within this sac provides cushioning, temperature regulation, and prevents desiccation during fetal development.
Structural Composition
- Structurally, the amnion consists of a single layer of flattened epithelial cells called amnioblasts.
- These cells are supported by an underlying basement membrane rich in collagen fibers.
- The outermost layer facing the chorion is lined with mesodermal cells that later fuse with chorionic mesoderm.
- Together with the chorion, they form what is known as the chorioamniotic membrane that surrounds and protects the fetus throughout gestation.
Functions of Amnion
- The primary function of the amnion is to provide mechanical protection against physical shocks or trauma.
- It also acts as a barrier against infections by preventing microorganisms from entering or leaving the gestational environment.
- Additionally, it facilitates fetal movement by reducing friction between tissues and allows for symmetric growth without adhesions.
Understanding how this delicate yet robust structure forms and functions sheds light on its indispensable role in prenatal development Selaput Pembungkus Embrio Salah Satunya Adalah Amnion Yang Mempunyai Fungsi. Amidst its simplicity lies an intricate system designed to nurture life within its protective embrace.
Amnion serves as a barrier against external factors, shielding the growing embryo from potential harm while allowing for essential exchanges of nutrients and waste products. This delicate balance is vital for the healthy development of the fetus Selaput Pembungkus Embrio Salah Satunya Adalah Amnion Yang Mempunyai Fungsi.






